Repetitive pointing task
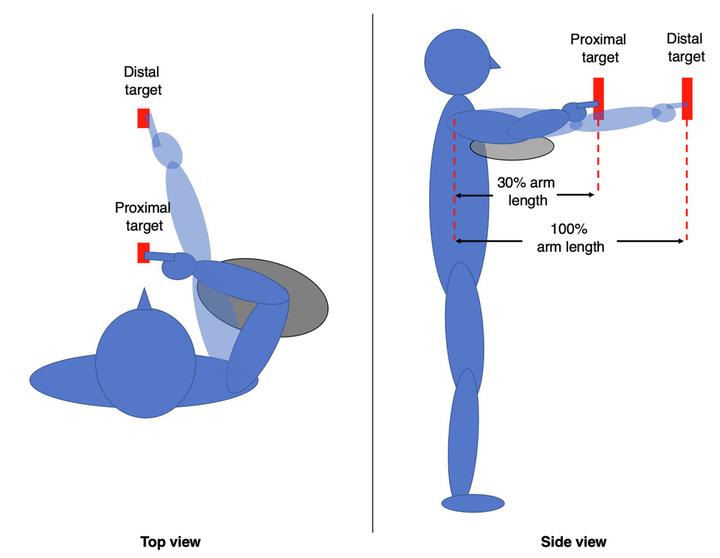
Female workers are at a greater risk for neck/shoulder musculoskeletal disorders. This project compared repetitive task-induced changes in muscular parameters between females and males. The outcome measures included muscle activity (via EMG), trapezius oxygenation (via NIRS), and muscle swelling (via ultrasonography). We found that females showed comparable fatigaiblity, oxygenation and majority EMG responses as males; however, females showed greater anterior deltoid activation and an absence of deltoid activation modulation with fatigue. For more details, please refer to studies below:
Yoon, S., Bailey, C. A., Cohen, N. R., & Côté, J. N. (2021). Changes in muscle activation, oxygenation, and morphology following a fatiguing repetitive forward reaching task in young adult males and females. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology, 102564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2021.102564
Yoon S, Bailey CA, Côté JN. Sex-specific muscle activation and oxygenation kinetics during a repetitive forward pointing task. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2021-0664